Bleeding Heart Flowers: Care Tips to Help Them Thrive in Your Garde
Introduction
A bleeding heart-shaped flower ( Dicentra spectabilis) is a stunning design for any garden. With its heart-shaped flowers hanging elegantly from arched branches, the plant radiates elegance and awe. But, as stunning as it is, maintaining and maintaining this plant requires careful attention to detail. This guide will take you through the essential information you need about growing, caring for, and bleeding hearts to ensure your garden will be a place of peace and beauty.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Bleeding Heart Flower
What Makes the Bleeding Heart Unique?
A bleeding heart is among the most stunning natural creations, often representing compassion, love and emotional connection. The distinctive heart-shaped flowers, complete with a teardrop-like edging create a stunning view in any garden with shade. The species are native to regions in Asia as well as North America, thriving in woodlands and in temperate climates. Their delicate form and graceful design add a romantic feel to any garden.
The bleeding hearts form clusters with slender stems that are with blooms that are adorned with shades of white, pink or red. Under the blooms, the plant’s fern-like leaves give it the appearance of depth and texture, making a striking contrast. With a height of two to three feet. These plants are ideal for the borders of woodland gardens or paths that are shaded. Their blooming time is the period from late spring through early summer, is the plants come to life at a time as other plants are waking up from their winter sleep.
Planting Bleeding Heart Flowers: The Foundation of Success
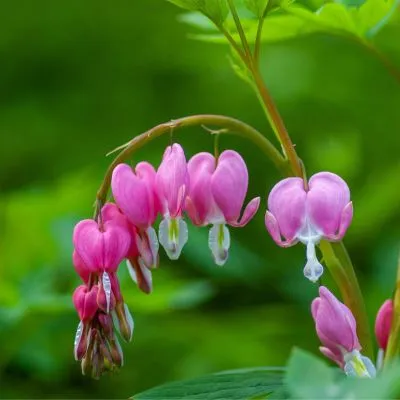

When to Plant
Timing is key when you are planting bleeding hearts. The ideal times to plant are in the autumn or early spring, as temperatures are cooler as well, and the soil is more workable. Planting at these times will allow roots to be established prior to the plant entering the growth phase. This is essential to ensure a healthy and strong beginning.
Choosing the Perfect Spot
Bleeding hearts are plants that love the shade. They are a good option for gardens that have little sunlight. You should look for areas that offer shades from partial to total, like under trees or in the vicinity of taller plants. A full-sun exposure can create stress, resulting in burnt foliage or the beginning of dormancy.
The most important instructions into consideration.
- Light: Partially to full shade is ideal to mimic the natural woodland environment.
- Soil: Choose a soil that is well-drained, moist and that is enriched with organic matter.
- Wind: Choose a shaded location to shield the stems’ delicate limbs from damaging winds.
Preparing the Soil
A healthy soil is the foundation of healthy plants like bleeding hearts. Begin by making the soil looser in the area you prefer and adding organic matter such as manure or compost. This helps improve drainage while providing the nutrients needed for vigorous development. Try to achieve a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0 that is slightly more acidic than neutral.
Bleeding Heart Flowers: Plant Profile
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Name | Bleeding Heart |
| Botanical Name | Dicentra spectabilis |
| Family | Papaveraceae (Poppy Family) |
| Plant Type | Herbaceous Perennial |
| Mature Size | It is 2 to 3 feet tall and 1 to 2 feet wide |
| Sun Exposure | Partial to Full Shade |
| Soil Type | Well-drained, Moist, Organic-Rich Soil |
| Soil pH | Slightly Acidic to Neutral (6.0–7.0) |
| Hardiness Zones | USDA Zones 3–9 |
| Native Area | Asia (China, Japan, Korea) and North America |
| Toxicity | Toxic to humans and pets if ingested (may cause nausea or vomiting) |
Caring for Your Bleeding Heart Flower
A proper care plan will ensure that the hearts of your loved ones are healthy each year. If you pay attention to their individual requirements, you will be able to enjoy their beauty and health with minimal effort.
Watering
Bleeding hearts require constant moisture in the soil, especially during active growth periods and blooming seasons. However, excessive watering can result in root rot, which is a common problem for this plant. To achieve the ideal balance, you should water thoroughly every week, either once or twice and ensure that it is moist but not soggy.
Tips to ensure that you are getting the most effective watering
- Seasonal adjustments: When there is a dry spell, increase the frequency of watering. In contrast, reduce the frequency when the plant is in dormancy in the summer.
- Timing: water early in the day to lessen the chance of fungal infections due to prolonged wet leaves.
Fertilizing
A bleeding heart that is fed well produces bright blooms as well as lush leaves. Apply an appropriate fertilizer (e.g. 10-10-10) in the springtime as the plant begins to grow. This will provide the essential nutrients needed to promote vigorous growth and blooming. Beware of over-fertilizing as it could cause over-growth of the leaves and a decrease in flowering.
- Frequency: Fertilize one time in early spring and once again when the first bloom is gone.
- Organic Alternatives: Organic plant food products can be used to improve soil over time.
Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning is vital to keep your bleeding heart tidy and healthy. When the blooming season is over, the plant’s foliage will begin to turn yellow and then die again. This is an expected part of the cycle, signalling the end of summer dormancy. In this period:
- Deadheading: Get rid of blooms that are no longer needed to encourage more blooms and also to stop seed formation.
- Cutting back: Cut back the yellowing stems until the ground to clean up the plant.
Seasonal Care
Hearts that are bleeding have special needs all through the year. In spring, concentrate on feeding and watering. When the plant is in summer dormancy, decrease irrigation and let the plant relax. In winter, you can mulch the base to protect the roots and avoid frost damage.
Propagation Techniques: Expanding Your Garden
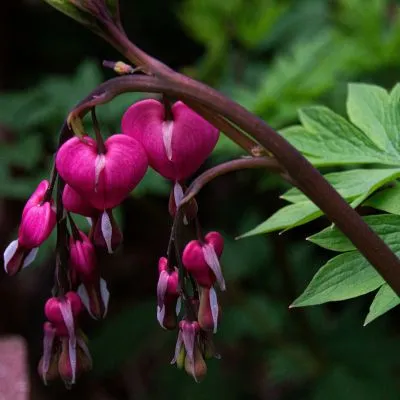

Making more bleeding hearts from your existing plants can be an exciting process. Three effective ways to propagate:
Division
The division is the most popular method of propagating bleeding hearts. It does not just create new plants, but it also helps prevent the overcrowding of plants, which could stress the plant.
Steps for division:
- When you divide plants: In the spring or in the fall, when they are in dormancy.
- What to do: I Dig Up the plant with care, making sure you don’t hurt the roots. Divide the root clumps into smaller pieces, each having the least one point of growth.
- Replanting: The divisions should be placed in the soil that has been prepared and follow the planting instructions.
Seed Propagation
The bleeding heart can also be cultivated from seeds, but this process requires patience. Seeds require an interval of cold stratification for them to be able to germinate.
Seed propagation steps:
- Harvest the seeds of mature plants following the flowering.
- Place it in a cool, humid place for 6 to 8 weeks.
- Sow the seeds in a well-drained soil. Keep them moist until they germinate.
Stem Cuttings
If you’d like a more rapid method, consider propagating using cuttings. Choose a 4-6-inch stem cutting during springtime, dip it into the rooting hormone, and then plant it in a container with an adequately draining medium. Keep the cutting in a shaded location until it starts to develop roots.
Managing Common Problems and Pests
The hearts that have bleeding are tough but aren’t immune to problems. Early detection and resolution of issues could save your plants.
Pests
- Aphids: suck sap from plants, causing weakening of the plant’s structure.
- Solution: Spray insecticidal soap or add ladybugs to your garden.
- Slugs and Snails: The species is known for chewing leaves; they’re an everyday nuisance in moist conditions.
- Solution: Diatomaceous Earth around the base or install beer traps.
Diseases
- Root Rot: It is caused by a swollen soil it is the most frequent problem.
- Prevention: ensures that the drainage is correct and does not overwater.
- Powdery Mildew: It is a white, fine powder that appears on the leaves.
- Solutions: Improve the circulation of air and treat it with a fungicide, if needed.
Enhancing Your Garden with Bleeding Hearts
Bleeding hearts don’t have to be standalone beauty items; they are also great when paired with other beauties. They are great with:
- Hostas: The big, bold leaves are stunningly contrasted with their delicate, bleeding hearts.
- Ferns: add texture and add to the nature-inspired look.
- Astilbes: Offer an additional wave of flowers following the bleeding hearts’ fade.
For landscaping, you can plant bleeding hearts along pathways that shade or in woodland gardens or in containers to be used for patios. They are versatile and are a good fit in any garden layout.
Conclusion: Cultivating Timeless Elegance
Care for the bleeding heart flower can be as rewarding as it is beautiful. The beautiful blooms, the strong symbolism and easy care, are wonderful features in any garden. With this advice, create an area that not only prospers but also tells a story of love, strength and natural beauty.
Do you want to fill your garden into a place of bleeding hearts? Get started now, and then share the story with your family and friends. A vibrant garden is a garden that brings happiness.
.